Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shen, X.*; Sun, Haomin; Deng, B.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 67(Part A), p.168 - 184, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:62.14(Thermodynamics)An experimental study on upward bubbly air-water flows in a vertical large-diameter square duct have been performed by mainly using four-sensor probes. Local measurements of interfacial area concentration (IAC), void fraction, 3D bubble velocity vector and bubble diameter at 3 axial positions were conducted. Although the interfacial area transport equation (IATE) and its bubble coalescence and breakup models have already played an important role in predicting the IAC in general two-phase flow fields, they are mainly developed based on the two-phase flow experimental data taken in round pipes or small diameter channels. To confirm their usability in large-diameter square duct, this study has evaluated the 1D one-group IATE with its 6 sets of bubble coalescence and breakup models with the presently-obtained database. It was found the relative error between the best prediction and the database was 25%.
Kozuka, Makoto*; Seki, Yohji; Kawamura, Hiroshi*
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 30(3), p.514 - 524, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:92.84(Thermodynamics)Direct numerical simulations of turbulent heat transfer in a channel flow are performed to investigate the effects of Reynolds and Prandtl numbers on higher-order turbulence statistics such as a turbulent Prandtl number and the budget for the dissipation rate of the temperature variance. The Reynolds numbers based on the friction velocity and the channel half width are 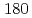 and
and 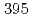 , and the molecular Prandtl numbers
, and the molecular Prandtl numbers 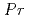 's 0.71-10.0. Careful attention is paid to ensure accuracy of the higher-order statistics through the use of a high spatial resolution comparable to Batchelor length scale. The wall-asymptotic value of the turbulent Prandtl number is mostly independent of Reynolds number for the current range of
's 0.71-10.0. Careful attention is paid to ensure accuracy of the higher-order statistics through the use of a high spatial resolution comparable to Batchelor length scale. The wall-asymptotic value of the turbulent Prandtl number is mostly independent of Reynolds number for the current range of 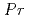 's. The budget for the dissipation rate of the temperature variance has been computed, and the negligible effect of a Reynolds number on the sum of all source and sink terms in near-wall region in the current computational range is found. This result is quite similar to the one in the budget for the dissipation rate of turbulent energy. In addition, a priori test for existing models is also performed to assess the
's. The budget for the dissipation rate of the temperature variance has been computed, and the negligible effect of a Reynolds number on the sum of all source and sink terms in near-wall region in the current computational range is found. This result is quite similar to the one in the budget for the dissipation rate of turbulent energy. In addition, a priori test for existing models is also performed to assess the 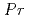 dependence on the individual terms and their summations in the budget.
dependence on the individual terms and their summations in the budget.